Weathernews’s second private microsatellite will observe natural phenomena like sea ice, typhoons and volcano eruptions.
Axelspace Corporation (HQ: Chuo-ku, Tokyo; CEO: Yuya Nakamura) and Weathernews Inc. announce today that the launch date of WNISAT-1R, the jointly-developed atmospheric and marine observation microsatellite, has been fixed for July 14, 2017. WNISAT-1R has completed all final operational checks and has already reached the launch site in Baikonur, Kazakhstan.
About WNISAT-1R
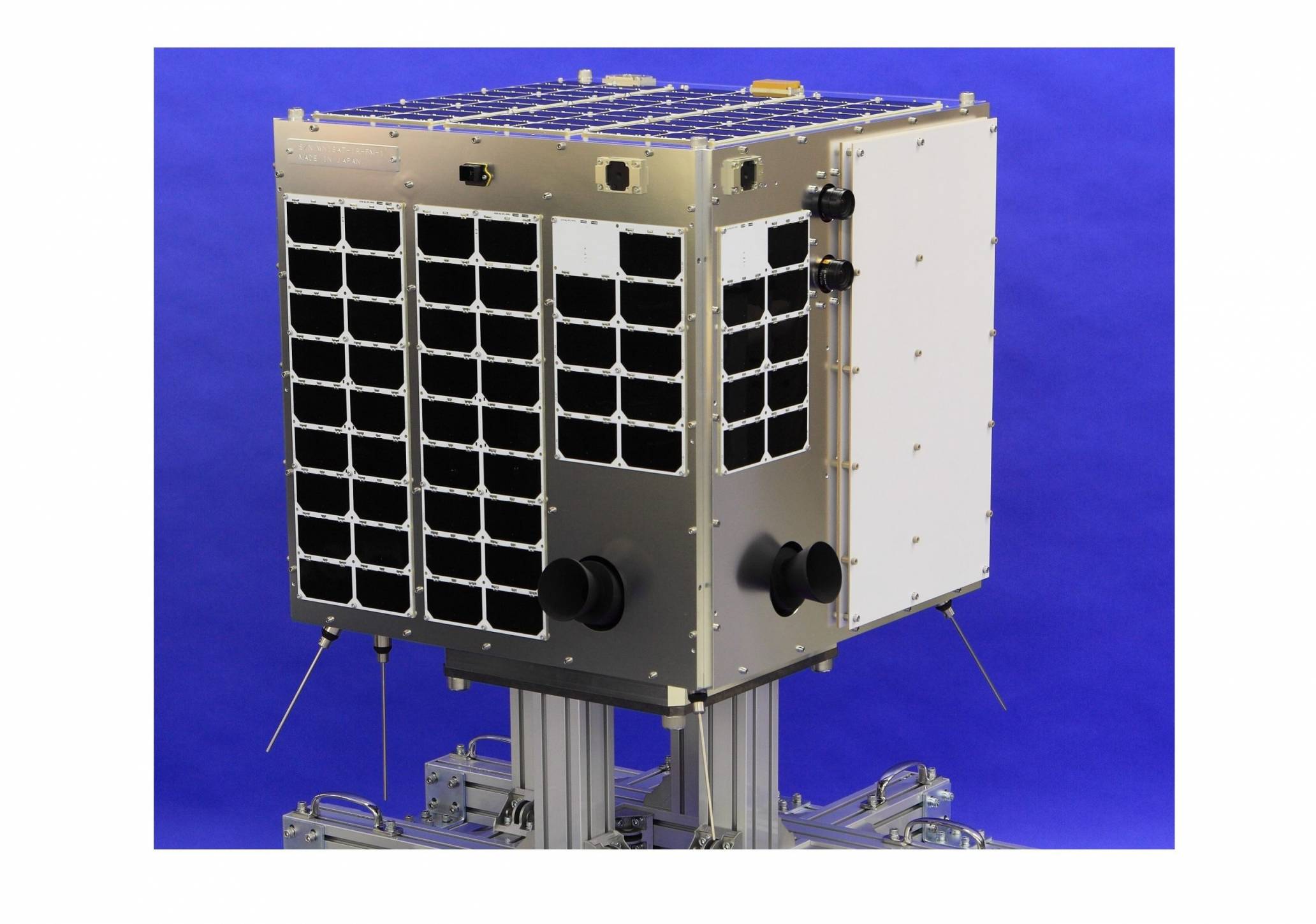
With a mass of 43kg, the microsatellite WNISAT-1R is equipped with an optical camera to observe atmospheric and marine natural phenomena. To provide high quality information about the best sea routes in places like the Bohai Sea (China) and the Gulf of Saint Lawrence (Canada) during the winter and the Arctic Sea during the summer, it is necessary to frequently measure the distribution of sea ice. The most effective way to do this is with a dedicated satellite in space, and WNISAT-1R has been built to be such a satellite. Developed jointly by Axelspace and Weathernews, it inherits and improves on its predecessor WNISAT-1, which was launched in 2013. Moreover, besides its main mission described above, WNISAT-1R has the following secondary missions:
Observation of natural phenomena like typhoons and active volcanoes anywhere on Earth. Thanks to its high attitude agility and to a completely automated operation regime, it is also able to respond promptly to emergency requests in case of natural disasters.
GNSS-R1 (Global Navigation Satellite System – Reflectometry) mission. GNSS-R takes advantage of the microwave signals emitted by navigation satellites, such as GPS, reflected by the surface of the Earth to determine the properties of the ground. Because microwaves are unaffected by clouds, this technology may detect ice distribution even when the sea is completely overcast. GNSS-R is an experimental mission, intended as a precursor for future, more advanced applications.
WNISAT-1R has been developed with the same bus technology that was used in Hodoyoshi-1, launched in 2014, and thus greatly surpasses the capabilities of WNISAT-1 while requiring a shorter development time and, consequently, lower costs.
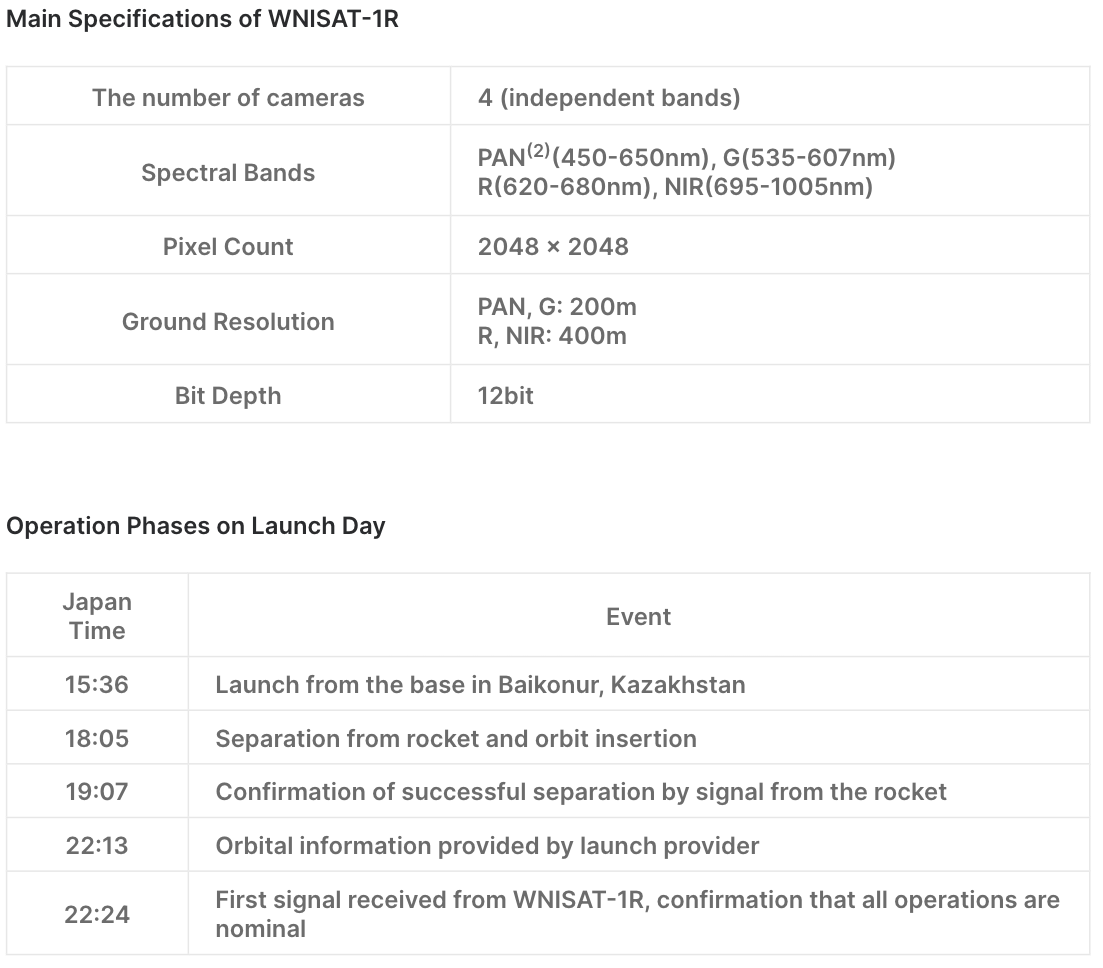

Glossary
1 GNSS: acronym standing for Global Navigation Satellite System. Besides the GPS constellation developed and operated by the United States, the term also covers other projects such as Russia’s GLONASS and Europe’s Galileo.
2 PAN: abbreviation of “panchromatic”. It refers to a single band that is sensitive to all visible wavelengths.
3 De-spin: control mode aimed at slowing down the spacecraft’s rotation and stabilizing its attitude.